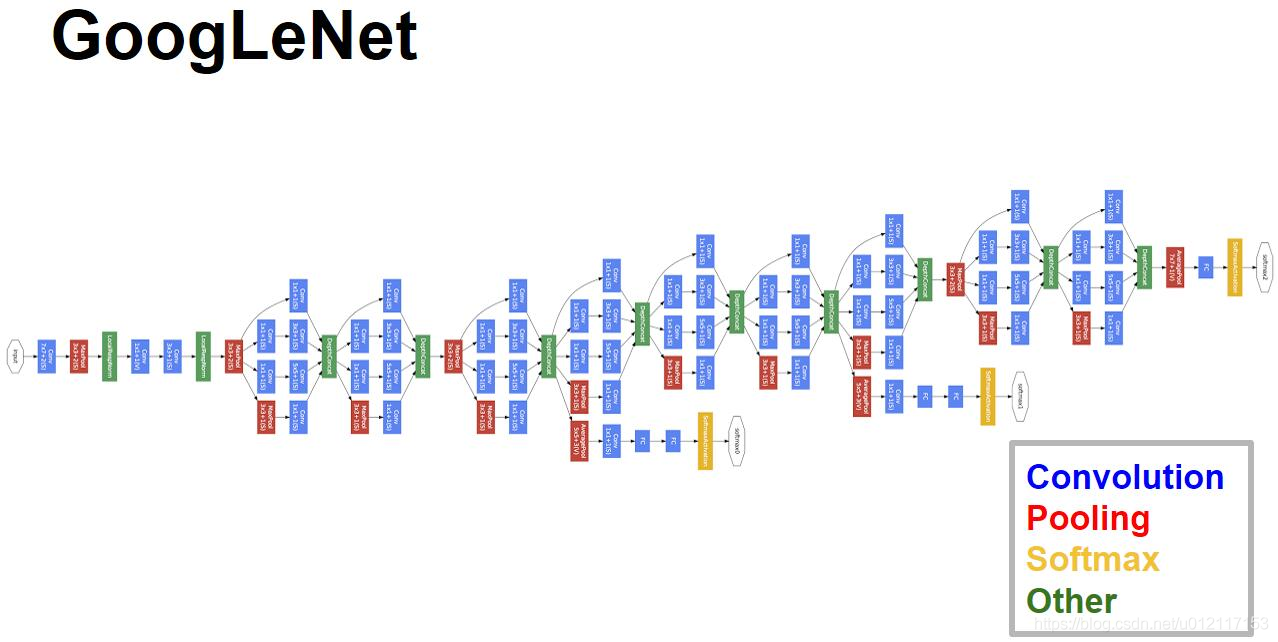
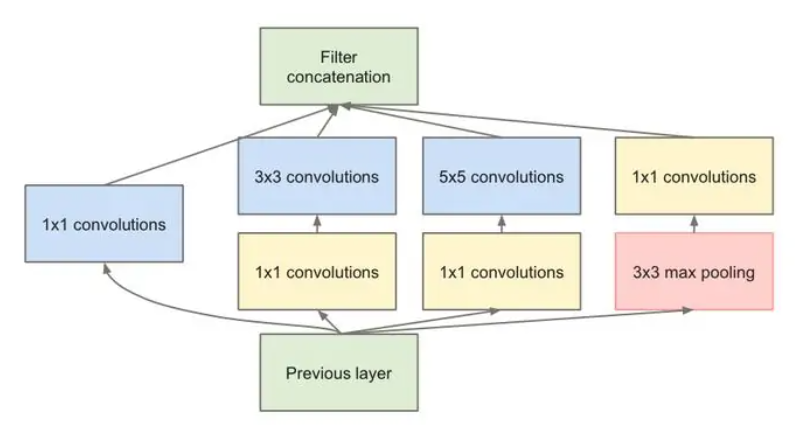
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| class GoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, auxiliary = True, init_weights = False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = auxiliary
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = Auxiliary(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = Auxiliary(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.maxpool2(x)
x = self.inception3a(x)
x = self.inception3b(x)
x = self.maxpool3(x)
x = self.inception4a(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
x = self.inception4c(x)
x = self.inception4d(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
x = self.maxpool4(x)
x = self.inception5a(x)
x = self.inception5b(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits:
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
|